Currently, this article is only available in German at integer-net.de →
But you can find an English practical summary of the series → in the Webguys Advent Calendar 2014.
Dipl. Inform. Fabian Schmengler | Magento Certified Developer | Magento Certified Solution Specialist
Currently, this article is only available in German at integer-net.de →
But you can find an English practical summary of the series → in the Webguys Advent Calendar 2014.
Did you ever wonder how Magento generates the increment_id values for orders, invoices etc. and how to use or extend this mechanism? Maybe you found the eav_entity_store table which contains the last increment id per entity type and store and possibly a different prefix per store:
mysql> select * from eav_entity_store; +-----------------+----------------+----------+------------------+-------------------+ | entity_store_id | entity_type_id | store_id | increment_prefix | increment_last_id | +-----------------+----------------+----------+------------------+-------------------+ | 1 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 100000090 | | 2 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 100000050 | | 3 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 100000027 | | 4 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 100000005 | | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 000000011 | | 6 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 200000001 | | 7 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 300000002 | | 8 | 8 | 3 | 3 | 300000001 | | 9 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 300000001 | +-----------------+----------------+----------+------------------+-------------------+ 9 rows in set (0.00 sec)
I will explain how to use this system in other entities in this article.
First of all, the standard method only works with EAV entities and only one attribute per entity can use the increment model and its name must be increment_id. I will explain later, how to overcome these limitations.
The increment_id attribute should have the backend model eav/entity_attribute_backend_increment and the entity itself needs some additional configuration;
$installer->installEntities(array(
'your_entity' => array(
'entity_model' => 'your/entity_resource',
'table' => 'your_entity_table',
'increment_model' => 'eav/entity_increment_numeric',
'increment_per_store' => 0,
'increment_pad_length' => 8,
'increment_pad_char' => '0',
'attributes' => array(
'increment_id', array(
'type' => Varien_Db_Ddl_Table::TYPE_TEXT,
'backend' => 'eav/entity_attribute_backend_increment,
),
// ... other attributes
),
),
));
Let’s have a look at the relevant fields:
eav/entity_increment_numeric and eav/entity_increment_alphanum or a custom model. More about custom increment models below.static as type instead.updateEntityType instead of installEntityTypeIf you set “increment_per_store” to “1” in the entity setup, the increment ids get prefixed with the store_id by default, if you set it to “0” (global), they get prefixed with “0”. To set up different prefixes, use the Mage_Eav_Model_Entity_Store model. The corresponding database table eav_entity_store shown above gets automatically filled with one entry per entity and store if the entity has “increment_per_store” set, otherwise with only one entry per entity with store_id 0.
The table contains the prefix as well as the last increment id (which both should be used by the increment model to determine the next id).
$productEntityType = Mage::getModel('eav/entity_type')
->loadByCode(Mage_Catalog_Model_Product::ENTITY);
$entityStoreConfig = Mage::getModel('eav/entity_store')
->loadByEntityStore($productEntityType->getId(), 0);
$entityStoreConfig->setEntityTypeId($productEntityType->getId())
->setStoreId(0)
->setIncrementPrefix($prefix)
->setIncrementLastId($lastId)
->save();
In this example, the global prefix (store=0) for the product entity is set to $prefix and the last id to $lastId. Usually this would only be called once from a setup script and once per store after store creation. Note that the automatically generated entries are only generated as soon as a new increment id for the according store is requested and no entry exists yet. The code is in Mage_Eav_Model_Entity_Type::fetchNewIncrementId():
public function fetchNewIncrementId($storeId = null)
{
...
if (!$entityStoreConfig->getId()) {
$entityStoreConfig
->setEntityTypeId($this->getId())
->setStoreId($storeId)
->setIncrementPrefix($storeId)
->save();
}
...
}
If we take a look at the backend model, we see that it checks if the object is new (i.e. does not have an id yet) and in this case delegates the increment id creation to the entity resource model itself:
/**
* Entity/Attribute/Model - attribute backend default
*
* @category Mage
* @package Mage_Eav
* @author Magento Core Team <core@magentocommerce.com>
*/
class Mage_Eav_Model_Entity_Attribute_Backend_Increment extends Mage_Eav_Model_Entity_Attribute_Backend_Abstract
{
/**
* Set new increment id
*
* @param Varien_Object $object
* @return Mage_Eav_Model_Entity_Attribute_Backend_Increment
*/
public function beforeSave($object)
{
if (!$object->getId()) {
$this->getAttribute()->getEntity()->setNewIncrementId($object);
}
return $this;
}
}
As you can see, the entity resource model does not get any information about the attribute itself and indeed, setNewIncrementId is hard coded to use the attribute increment_id (getIncrementId() and setIncrementId()):
/**
* Set new increment id to object
*
* @param Varien_Object $object
* @return Mage_Eav_Model_Entity_Abstract
*/
public function setNewIncrementId(Varien_Object $object)
{
if ($object->getIncrementId()) {
return $this;
}
$incrementId = $this->getEntityType()->fetchNewIncrementId($object->getStoreId());
if ($incrementId !== false) {
$object->setIncrementId($incrementId);
}
return $this;
}
There are two ways to overcome this limitation:
setIncrementId() and getIncrementId() in your entity to access the actual incremented attribute.beforeSave() to assign the generated increment id to the actual attribute afterwards. A simple version could look like this:
class Your_Awesome_Model_Entity_Attribute_Backend_Increment extends
Mage_Eav_Model_Entity_Attribute_Backend_Increment
{
public function beforeSave($object)
parent::beforeSave($object);
$object->setData($this->getAttribute()->getName(), $object->getIncrementId());
return $this;
}
}
As you probably know, orders, invoices etc. are no EAV entities 1 but they still have entries in the entity_type table and use increment ids. If they can, you can too, so let’s see how it has been done for orders.
The entity type is registered just as a real EAV entity:
/**
* Install eav entity types to the eav/entity_type table
*/
$installer->addEntityType('order', array(
'entity_model' => 'sales/order',
'table' => 'sales/order',
'increment_model' => 'eav/entity_increment_numeric',
'increment_per_store' => true
));
Because there is no EAV attribute that could use the backend model, setting the increment id must be triggered from the order model itself:
protected function _beforeSave()
{
...
if (!$this->getIncrementId()) {
$incrementId = Mage::getSingleton('eav/config')
->getEntityType('order')
->fetchNewIncrementId($this->getStoreId());
$this->setIncrementId($incrementId);
}
...
}
And that’s it!
You can specify any class as increment model that implements Mage_Eav_Model_Entity_Increment_Interface. Be aware: This interface pretents to only need one method, getNextId(), but at least the following setters will be called as well:
setPrefixsetPadLengthsetPadCharsetLastIdsetEntityTypeIdsetStoreIdYeah, Magento doesn’t give much love to interfaces. So if you want to implement your own increment model, you should at least inherit from Varien_Object, better from Mage_Eav_Model_Entity_Increment_Abstract which already provides you with the prefix and padding logic.
In the method getNextId() you will then generate the next increment id based on the last one, that is accessible with $this->getLastId()
A real-life example is my AutoSKU extension, which assigns product SKUs automatically. To achieve this, I set up an increment model for the catalog_product entity, changed the backend model of the SKU attribute, set it to be not required and made it uneditable. Check out the Github repository for implementation details:
https://github.com/schmengler/AutoSKU Continue reading “Magento Tutorial: How to Use Increment Models to Generate IDs (or SKUs)”
Notes:
On March 7th and 8th FireGento presents the first Mage Unconference for Clients, Merchants, Agencies, Service-Providers – and for sure – Developers. The Schedule of the Unconference is whatever the attendees make out of it.
>>> Get our Ticket now and be part of the Community on March 7th and 8th, 2015 in Berlin! <<<
I will be there! If you are interested, don’t wait too long before the event gets cancelled due to not enough tickets being sold!
I worked on a website where many images should have an inner shadow. To not need to edit all of them in Photoshop, the “inset” value for the CSS3 attribute “box-shadow” came in handy, but it cannot be applied to images without more ado. I want to show my solution here.

Applied directly on img elements, the shadow stays behind the image, so it is only visible at all if the image has transparency. If you add a wrapper element which gets the shadow, it is still behind the image but can be positioned with z-index. Unfortunately the image has to be moved to the back, moving the wrapper to the front is not possible 1:
<div class="box-shadow">
<img src="/images/graphic.jpg" />
</div>
.box-shadow {
box-shadow: 0 0 10px 6px white inset;
}
.box-shadow img {
position: relative;
z-index: -1;
}
The problem with this code is that the image is not only placed behind the wrapper but behind all other elements in the same Stacking Context. Which elements form a stacking context is described quite well in the Mozilla Documentation:
- the root element (HTML),
- positioned (absolutely or relatively) with a z-index value other than “auto”,
- a flex item with a z-index value other than “auto”,
- elements with an opacity value less than 1. (See the specification for opacity),
- elements with a transform value other than “none”,
- elements with a mix-blend-mode value other than “normal”,
- elements with isolation set to “isolate”,
- on mobile WebKit and Chrome 22+, position: fixed always creates a new stacking context, even when z-index is “auto”
- specifing any attribute above in will-change even you don’t write themselves directly
In this case it was applicable to assign a z-index and relative positioning to the direct parent element of the wrapper (let’s call it #parent):
#parent {
position: relative;
z-index: 0;
}
If this is not possible, e.g. because it needs a different position value or the z-index has unwanted side effects, I would use opacity instead, with a value of almost 1, so that no effect is visible but it still creates a stacking context.
#parent {
opacity: 0.999;
}
Related post on StackOverflow Continue reading “[CSS] Inset Box Shadow On Image”
Notes:
It’s simple and elegant, since PHP 5.4 introduced short array syntax:
$everySingleArrayInitializationFromNowOn = [];
Why this step? An alarming large amount of websites still runs on PHP 5.3, which does not get updated anymore since 2014/08/14, after one year of “security only” support. In other words, the next critical security hole will only be fixed for versions above 5.4. By the way, active development of the PHP 5.4 branch was discontinued on 2014/09/14. it’s already in the “security only” phase. On 2014/08/28, PHP 5.6 has been released, on 2013/06/20, almost 1.5 years ago, PHP 5.5.
So, by now, in the year 2014 everybody should work on PHP 5.5, right? That’s the theory, in practice it looks like this:
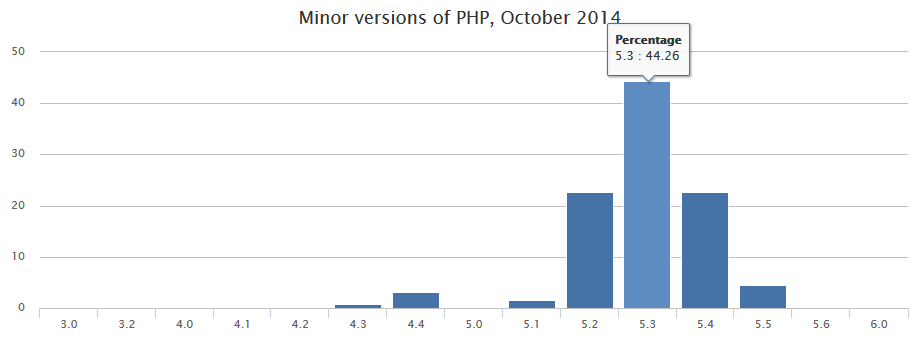
Source: http://blog.pascal-martin.fr/post/php-versions-stats-2014-10-en
Almost half of the Alexa Top 1M Sites that run on PHP, state the version 5.3, ca. one quarter even 5.2, which is not supported since Jan. 2011. PHP 5.2.17 even is the most used patch version in this statistic.
There are probably many reasons:
I want to go into some background briefly.
Continue reading “Why I Am Actively Going to Drop PHP 5.3 Compatibility”
Currently, this article is only available in German at integer-net.de →
But you can find an English practical summary of the series → in the Webguys Advent Calendar 2014.
Currently, this article is only available in German at integer-net.de →
But you can find an English practical summary of the series → in the Webguys Advent Calendar 2014.
This question came up on Magento.SE and more people should know, how dead simple it actually is.
If you look at core/Mage/Checkout/etc/config.xml you can see how Magento defines for the checkout to use the secure base URL, i.e. HTTPS:
<frontend>
<secure_url>
<checkout_onepage>/checkout/onepage</checkout_onepage>
<checkout_multishipping>/checkout/multishipping</checkout_multishipping>
</secure_url>
</frontend>
That’s all. You can configure your own controllers to use the secure URL in the same way and now Mage::getUrl() returns the secure URL for the configured routes and any unsecure request will be redirected.
A Magento-Bug, that circulates in the Magento forums on and StackOverflow for some years, is that tier prices do not work properly together with bundle products. Over time there was some improvement but as for today (Magento CE 1.9) the following still does not work:
There are some suggestions found on the web but more questions than answers, so I created a (hopefully) complete solution without core hacks and with only minimally invasive class rewrites. Until Magento gets it solved itself, you can use this module to enable bundles with tier prices:
SGH_BundleTierPrices (tested in Magento CE 1.8 and Magento CE 1.9)
Continue reading “Magento Bundle Products: Use Tier Prices of Simple Products”
If you want to change the allowed image extensions for product images in Magento you will find out that they are hard coded in Mage/Catalog/Model/Product/Attribute/Backend/Media.php and Mage/Adminhtml/controllers/Catalog/Product/GalleryController.php
However, I found an observer that allows you to change them along with other configuration of the uploader. This post explains how to create an extension to allow uploading of SVG files. Foundations of Magento extension develoment are presumed.